Potassium sorbate is a chemical preservative that is found in many food products. An effective preservative in acidic conditions, potassium sorbate typically presents as a white crystalline solid and is ideally used as a food additive because of its tasteless and odorless quality. As people become more wary about the ingredients they consume, some might wonder if whether potassium sorbate is vegan.
Since potassium sorbate is produced without the involvement of any animal product or derivative, the chemical preservative is completely for vegans and their lifestyle. Essentially the potassium salt of sorbic acid, potassium sorbate is synthetically produced from precursor chemicals and is widely used in the food industry.
Food preservatives are necessary agents used in the food industry for prolonging shelf-lives of food products and protecting them from spoilage-causing microorganisms. One such preservative used is potassium sorbate.
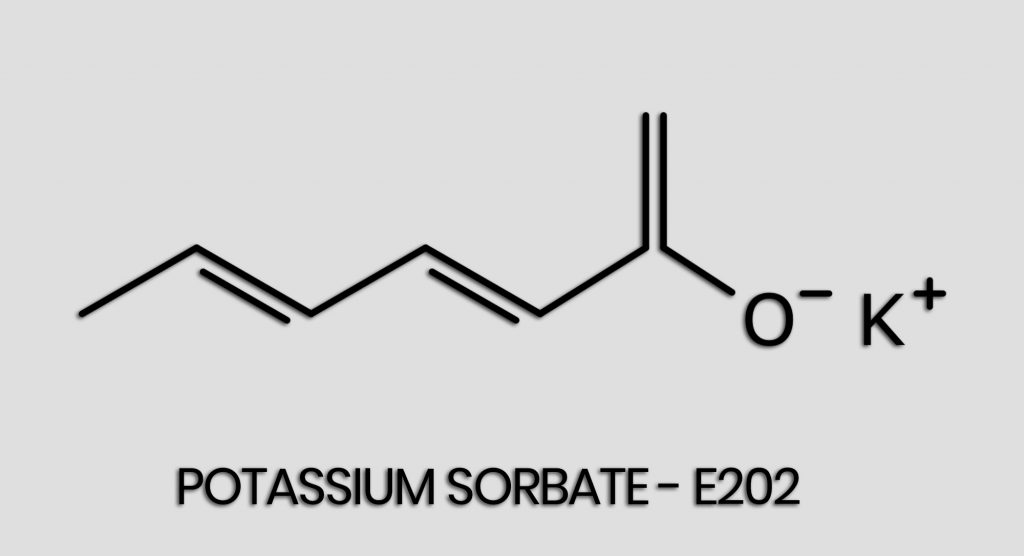
Potassium sorbate, the potassium salt of sorbic acid, is a common food additive that is conventionally used as a chemical preservative. Denoted by the chemical formula C6H7KO2, potassium sorbate can also be listed in the ingredients list by its E number: E 202 (1).
Specifically, potassium sorbate functions as an effective preservative by inhibiting the growth of microorganisms that are associated with spoilage such as certain bacteria, molds, and yeasts.
Potassium sorbate is an ideal chemical preservative for food that is slightly acidic as potassium sorbate is more effective at lower pH (specifically, 3-6.5).
Several mechanisms have been suggested for the mode of action of potassium sorbate. First, the food additive can inhibit microbial growth by disrupting cell membrane and integrity. Potassium sorbate has also been known to disrupt transport functions and metabolic activity (2).
Aside from as a chemical preservative, potassium sorbate is also commonly used in the wine industry as a wine stabilizer. Wine is essentially produced through fermentation with the help of yeasts. Once the wine has reached the desired point in its fermentation, potassium sorbate is used to inactivate the yeast and halt the fermentation from proceeding.
Due to its antimicrobial capabilities, potassium sorbate can also be found to be used in personal care items such as contact lens solutions, shampoos and moisturizers, and eyeshadow and other cosmetics.
The antimicrobial activity of potassium sorbate can be attributed to the presence of its carboxyl group (-COOH) and the number of carbon atoms in its structure. Previous studies have suggested that food additives with shorter chains such as potassium sorbate and sodium acetate are more effective antimicrobials compared to additives with long carbon chains.
Potassium sorbate is completely vegan since its production does not involve any animal product or derivative. Practically all the potassium sorbate in the food industry is synthetically produced.
While the vegan community is composed of a diverse mix of subpopulations with specific restrictions, most vegans should be okay with potassium sorbate.
The main proponent of potassium sorbate is sorbic acid. While sorbic acid is a naturally occurring acid found in the unripe berries of the Rowan tree (Sorbus aucuparia), it is also typically synthesized in the lab by condensing malonic acid and trans-butenal. It can also be produced from the condensation of crotonaldehyde and ketene.
Potassium sorbate is conventionally produced by reacting equal parts of sorbic acid and potassium hydroxide. The final product is then crystallized from an aqueous solution of ethanol.
Potassium sorbate is an excellent chemical preservative which is why it can be found in a wide variety of products, especially kinds that do not necessarily have long shelf-lives. Since the natural pH of potassium sorbate is about 4.5, the chemical preservative is better utilized for acidic food products. The effectiveness of potassium sorbate decreases as the pH increases which is why it is not recommended for alkaline food items.
Examples of food products that might contain potassium sorbate include cheese, cheese-related products, ice cream, yogurt, soft drinks and juices, apple cider, wine, baked goods, canned fruits and vegetables, dried fruits, dried meats, and pickles.
Potassium sorbate is generally considered to be safe and is approved for human consumption by various food safety authorities. The safety certification imposed by these food safety authorities is based on evidence from numerous safety studies and the opinions of experts in food safety.
The FDA (Food and Drug Administration) regards potassium sorbate as GRAS (generally recognized as safe) as long as the substance is in accordance with good manufacturing (3).
On the other hand, the EFSA (European Food Safety Authority) re-evaluated the safety of potassium sorbate in 2019. Although the food safety authority still views potassium sorbate to be safe for consumption, they modified the acceptable daily intake (ADI) to be 11 milligrams of potassium sorbate per kilogram of body weight (4).
This is actually an increase in safety confidence as the EFSA established the ADI of potassium sorbate to be only 3 milligrams per kilogram body weight back in 2015 (5).
Exposure (e.g., contact to eyes and skin, etc.) with pure potassium sorbate can lead to irritation. However, potassium sorbate used in the food industry is often very minimal to the point of negligible concern. In the USA, the authorized limit of potassium sorbate is 0.03%.
Furthermore, the human body does not accumulate potassium sorbate. Potassium sorbate participates in the normal fat metabolism in the human body which means it is oxidized into carbon dioxide and water.
References
1. https://www.sciencedirect.com/
2. https://efsa.onlinelibrary.wiley.com/
3. https://www.accessdata.fda.gov/
